An ICT Order Block and a Breaker Block are key concepts in the Smart Money Concept (SMC) trading methodology developed by Michael Huddleston, also known as the Inner Circle Trader (ICT).
This article provides a practical guide with examples, explaining what an Order Block and a Breaker Block are, why they are effective, how to spot them on a chart, and, most importantly, how to use them successfully in trading.
Read more:
Disclaimer: The ATAS company is not affiliated with Michael Huddleston (Inner Circle Trader) and does not promote or endorse his trading strategies. This article discusses the popular ICT Order Block and Breaker Block patterns and highlights ATAS platform tools that may be helpful for traders exploring the Smart Money Concept.
What Is an Order Block (OB) in Trading?
An Order Block (OB) is a pattern that occurs at price reversals. It can be either bullish (Bullish Order Block) or bearish (Bearish Order Block).
Although ICT tends to avoid trading cryptocurrencies, his patterns can be applied across any timeframes on forex, stock, and commodity markets.
ICT Order Block Definition
A Bullish Order Block forms from a bearish candle if the following three conditions are met:
✔ This bearish candle is the lowest among all bearish candles formed during the price decline.
✔ The candle closes near its low (in the lower half of the candle).
✔ There is a support level nearby (though this condition can sometimes be omitted).
The screenshot below, provided by ICT, illustrates how a Bullish Order Block forms.
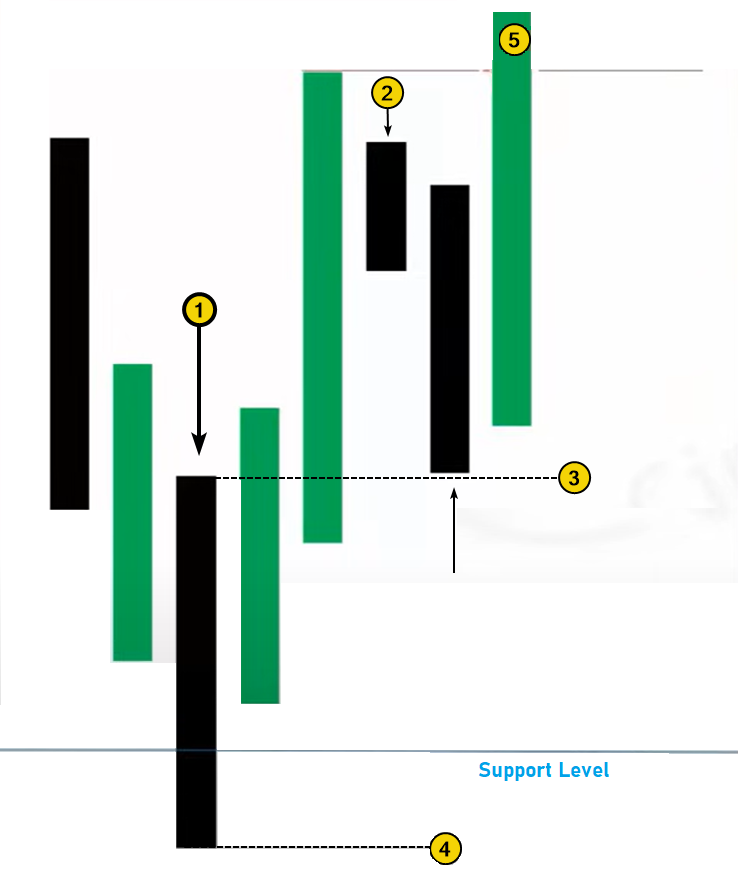
Arrow #1 points to the bearish candle:
- on the left, there is a price decline period;
- then, the price reverses upward from the support level.
An area extending to the right from this candle is called the Order Block.
How to trade an Order Block
The rules for trading Order Blocks are quite simple. Let’s look at them using the example of a Bullish Order Block, as shown in the diagram above. A signal to open a long position is triggered when the following conditions are met:
- After the Order Block forms, the price moves higher. The candle marked with number 2 is positioned entirely above candle 1 (its upper boundary is marked by level 3).
- The price then pulls back to level 3, generating a signal to enter a long position.
- The stop-loss is placed below the Order Block (marked by level 4).
- The take-profit is placed above the local high (5), though more ambitious targets can also be considered.
The same rules apply in reverse for a Bearish Order Block.
At its core, an Order Block (OB) is a support or resistance area that extends from a bearish or bullish candle, with the close near the low or high. It points to a possible trend reversal from a support or resistance level.
Example of a Bullish Order Block on a Real Chart
In the screenshot below, from the official Smart Money Concept YouTube channel, Michael Huddleston demonstrates an example of his Order Block pattern on the U.S. Dollar Index futures chart.

The numbers indicate:
(1) a support level from a key low on the left.
(2) a bearish candle, from which the Bullish Order Block zone extends to the right after two black candles. In this case, the upper boundary of the zone is drawn from the candle’s opening price, although some sources allow the upper boundary to be drawn from the candle’s high.
(3) a candle entirely above the Order Block zone, which acts as confirmation.
(4) a long entry signal is generated when the price dips into the Bullish Order Block zone.
For more examples of identifying Order Blocks, check out this video on Smart Money Concept on our channel:
Next, we will explore why Order Blocks work and provide more examples of trading using Order Block signals, with explanations on footprint charts.
Why Do Order Blocks Work?
Let’s say you are a Smart Money trader and are confident that the price of an asset will rise soon for several reasons, such as:
- insider information suggests that upcoming economic news will be bullish;
- analysts believe the asset is currently undervalued.
You decide to open a long position, but there is a problem: you are dealing with large volumes. If you place a large buy order at market price, it will push the price higher, which is not profitable for you.
Therefore, you need a downtrend (liquidity from sellers) that you can “meet” with your limit buy orders (Order Blocks). This increases your chances of opening a large long position near the price low. Buying at lows and selling at highs is the typical strategy used by Smart Money participants.
As Tom Williams, the creator of the VSA strategy, often said: professionals always buy during downtrends and sell during uptrends. You can learn more about this in our series of articles on Volume Spread Analysis, with the first one available here.
How to Identify an Order Block Using Volume Indicators
Although Michael Huddleston (aka ICT) does not use additional indicators in his trading, we will show how tools like the vertical volume indicator (including the delta indicator) and the market profile indicator can provide valuable confirmations when trading Order Blocks.
Example: The screenshot below shows a Bullish Order Block and a Bearish Order Block on a 15-minute chart of the euro futures:
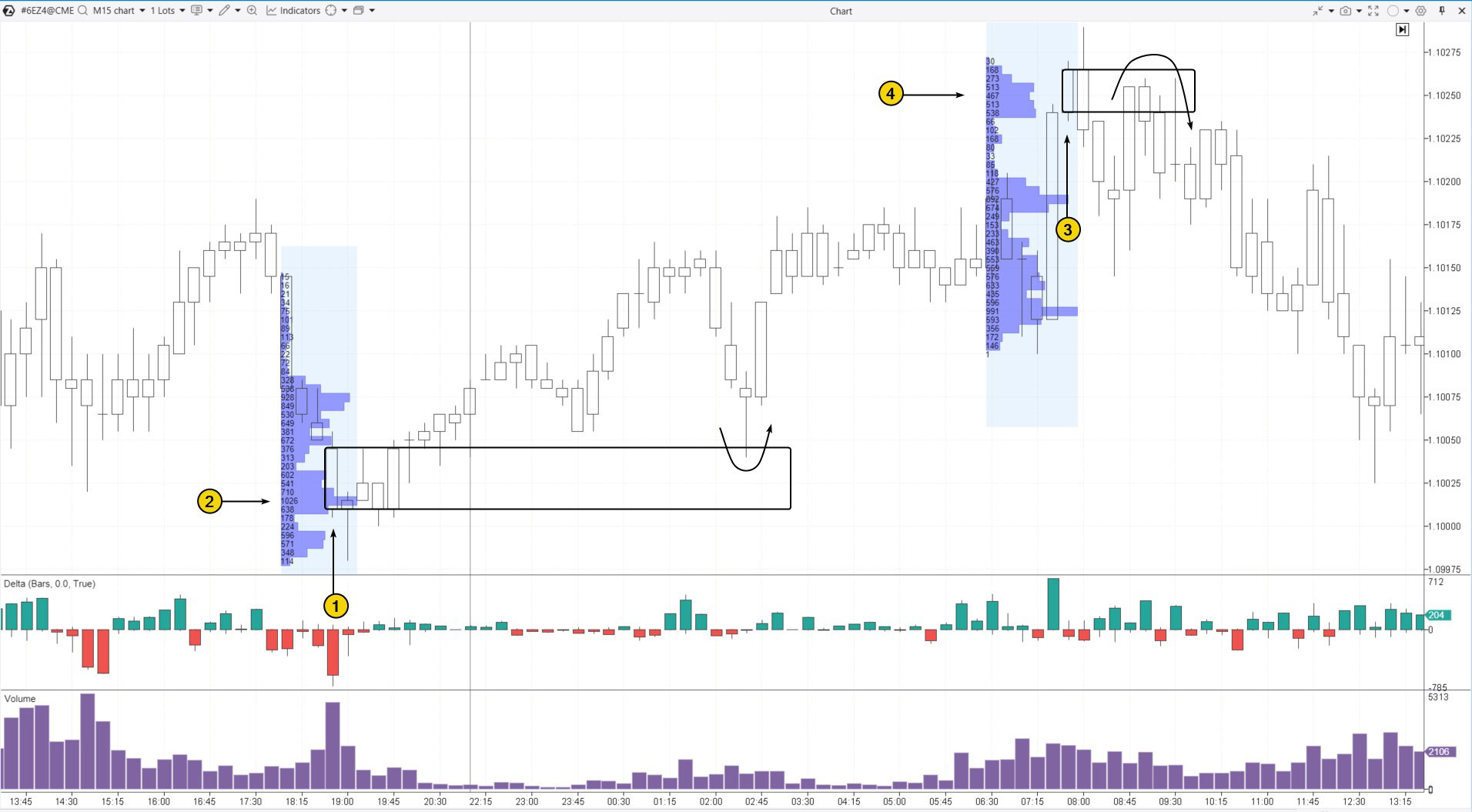
The first Order Block is bullish. It formed as the price dropped to the support level near the psychological level of 1.10000.
Number 1 marks the bearish candle from which the Order Block support zone extends to the right (highlighted by a rectangle). Note the spike in negative delta: it suggests that retail traders were actively placing sell market orders. However, the market profile shows a (2) bulge — what might this indicate? Perhaps the presence of a cluster of Limit-Buy orders holding the price from falling? It is reasonable to assume these were better-informed professionals (Smart Money), building long positions with limit buy orders.
The subsequent price rise confirmed the bullish pattern, and the test of the Order Block zone at the 02:30 candle (shown by the arrow) could have been used to enter long positions.
The following day, a second Order Block emerged, this time a bearish one. It formed from the candle marked as (3). It is important to note that, at this chart scale, the resistance level is not clearly defined. However, we can find confirmation through the following indicators:
- the bulge on the profile (4) indicates executed Sell-Limits placed by Smart Money participants, capitalizing on the price surge during the 07:30 candle;
- the subsequent price decline over the next two candles below the Order Block area.
The arrow highlights the price returning to the Bearish Order Block, which could have been used to open short positions.
How to Trade Order Blocks Using Footprint Charts
Footprint charts (also known as cluster charts) are one of the most informative tools available to traders, allowing for an in-depth analysis of market participants’ actions. In the context of the Smart Money Concept, footprint charts not only help identify Order Blocks but also visually illustrate how events unfold during the formation of these patterns.
Before we delve into examples of trading Order Blocks using footprint charts, let’s summarize the trading rules for this pattern.
Order Block Trading Strategy: A Step-by-Step Approach
Step 1. Identify the pattern. This involves:
- for a bullish pattern: look for a bearish candle near a support level;
- for a bearish pattern: search for a bullish candle near a resistance level.
Indicators such as Delta, market profile, and other ATAS volume analysis tools can aid in the identification of Order Blocks.
Step 2. Confirmation. This step involves the price beginning to show signs of reversal as it bounces off a support or resistance level.
Step 3. Entry. You should enter a position when the price returns to the Order Block area (in other words, when it tests the area).
Step 4. Establish exit targets.
- The ICT recommends placing the stop-loss beyond the candle from which the Order Block area forms.
- The take-profit level is determined subjectively. At a minimum, it can be an intermediate extreme formed prior to the test of the Order Block area. Ideally, the potential profit should exceed the risk taken.
Bearish Order Block on the Footprint Chart
The screenshot below demonstrates an example of a Bearish Order Block that formed in early October 2024, using data from the futures market for BNB on Binance Futures.

In the chart, the local peak is indicated by (1), which represents the current resistance level. To the left (not visible due to the selected chart scale), there is another peak at approximately the same level.
During the attempt to break above peak (1) on candle (2), we observe a spike in positive delta, signaling buyer activity that interpreted the price action as the start of a new bullish trend. The clusters within the candle are almost entirely green, which could also reflect an “emergency” closing of short positions, either manually or via stop-loss orders.
However, despite this market buying activity, the price subsequently declines (3). Why? The surge in market buys creates the necessary liquidity for Smart Money participants to execute their large-volume limit sell orders. As a result, we have the basis to:
✔ create a Bearish Order Block resistance area to the right of candle (2);
✔ open a short position when the price retraces back to the marked area the following day.
Analyzing vertical volumes provides greater confidence for entering short positions. Market buying activity (4) has diminished, and overall volumes are declining, indicating a lack of participants willing to pay such high prices for BNB.
This scenario represents a classic pattern known as a bull trap, or upthrust in VSA terminology (6), which often signals the beginning of a price decline.
Bearish Order Block on AAPL Stock Price Chart
In the summer of 2024, a sell setup based on the Order Block pattern emerged on the daily chart for Apple (AAPL) stock:

Following the announcement of Apple Intelligence on June 11, sentiment turned extremely bullish: AAPL shares broke through the psychological barrier of $200 and continued to rise (1), reaching new all-time highs until hitting $230.
It is important to note the candle on July 10 and its profile, as well as the significant decline of the July 11 candle, which closed well below the $230 level. This can be seen as a temporary surge in demand on July 10 that quickly faded the following day.
On July 15, the price soared above $235 after Morgan Stanley raised its target price for the stock, and Market Watch reported that the price could potentially reach $300. These positive headlines created a wave of enthusiastic demand, but… who sells at the top when the market is filled with such obvious optimism? Smart Money.
Following ICT rules, the resistance area of the Bearish Order Block can be extended to the right after the price declines (3). The test of this area on August 29 (4) offered a chance to enter a short position. This opportunity was reinforced by the candle’s shape, which resembled an inverted hammer and closed below the trading activity level identified in the profile. It seems that Smart Money still considered $230 to be too high for AAPL.
Example of a Breaker Block
What is a Breaker Block in trading? It is a situation when an Order Block area does not lead to a price reversal and the price breaks through it instead.
According to Smart Money Concept rules, this happens as follows:
- a Bullish Order Block forms on the chart;
- when the price tests this support zone, instead of reversing upwards, it breaks below;
- in this case, the Bullish Order Block turns into a Breaker Block, and it is expected to act as resistance.
This concept is similar to the idea of mirror levels in trading: previous support becomes resistance after a breakout, and former resistance turns into support. In the same way, a Bearish Order Block, when broken to the upside, transforms into a Breaker Block and may later provide support.
An example of a Breaker Block is shown below on the daily chart of QQQ, a financial instrument that tracks the Nasdaq index.

In mid-August (1), the price was approaching a resistance level (2), which could be identified by the bulge on the volume profile. On August 20 and 21, the vertical volumes were low during the price’s upward move (indicating weak buyer activity), but on August 22, a noticeable price drop occurred with increasing volume — a clear sign of sellers stepping in and shifting market sentiment.
As the price moved lower in early September, it created the foundation for a bearish Order Block zone (highlighted in yellow), setting up an expected test.
By mid-September, the price started to show signs of a bearish reversal (3) from this resistance zone, but the attempt failed when the September 19 candle opened above it. This indicated that the yellow zone had turned into a potential Breaker Block. At this point, the next step was to wait for the candles to fully settle above the zone, which happened on September 25. Following the ICT Smart Money Concept rules, the yellow area was now expected to act as support.
This expectation was fulfilled in October when the price made a bullish reversal (4) during the test of the Breaker Block zone.
FAQ
What is an Order Block in trading?
Order Block (OB) in trading refers to a zone where major market players (institutional investors) place large buy or sell orders, which can either halt or reverse the current trend.
What types of Order Blocks exist in the Smart Money trading concept?
✔ A Bullish Order Block is formed from a bearish candle and indicates a potential upward reversal when the area is tested.
✔ A Bearish Order Block is formed from a bullish candle and indicates a potential downward reversal when the area is tested.
✔ Breaker Block appears when, upon testing an Order Block, the price does not reverse. In this case, it is considered that the support area shifts to resistance, and vice versa.
What does an Order Block look like in crypto?
In both the cryptocurrency and forex markets, a Bullish Order Block is a zone extending from a bearish candle that closes near its low, followed by an upward price reversal (though this might not happen right away). A Bearish Order Block works the opposite way.
How does the Order Block trading strategy work?
Order Blocks help traders identify key support and resistance areas. Traders use them to open positions when the price tests these zones.
Why are Order Blocks important?
They help traders align in the same direction as Smart Money.
Is trading Order Blocks profitable?
Trading based on Order Blocks can be profitable if these zones are correctly identified and the market context is taken into account. The key to a successful strategy is understanding where institutional players place large orders. Tools like market profile, footprint charts, and other ATAS volume analysis indicators can be helpful in this process.
What is the difference between an Order Block and a fair value gap?
Both concepts are part of the Smart Money Concept. The difference is that Order Blocks focus on price reversals driven by Smart Money activity, while a FVG (Fair Value Gap) refers to an impulsive price movement caused by an imbalance between buyers and sellers. For more details, check out the article: What Is a Fair Value Gap and How to Trade It?
Is an Order Block the same as support and resistance?
Not exactly. Support and resistance are broader concepts, and Order Block zones are a more specific example within that framework.
How to Learn Trading with Order Block Patterns
When viewing the Order Block pattern as a candlestick formation, beginners often encounter several challenges in practice:
✔ the zones can be either too narrow or too wide;
✔ Order Blocks may appear infrequently, especially on daily timeframes;
✔ there is the risk of false signals, as candle sequences that resemble the ICT Order Block pattern might form on the chart without indicating actual Smart Money activity.
This highlights the importance of using additional volume analysis tools for confirmation.
To see if you can trade Order Block patterns profitably, try the ATAS Market Replay simulator for traders. This module of the ATAS platform uses historical data to recreate real-time trading conditions. Therefore, you can practice without any financial risk and learn to trade various strategies, such as the ICT Fair Value Gap pattern.
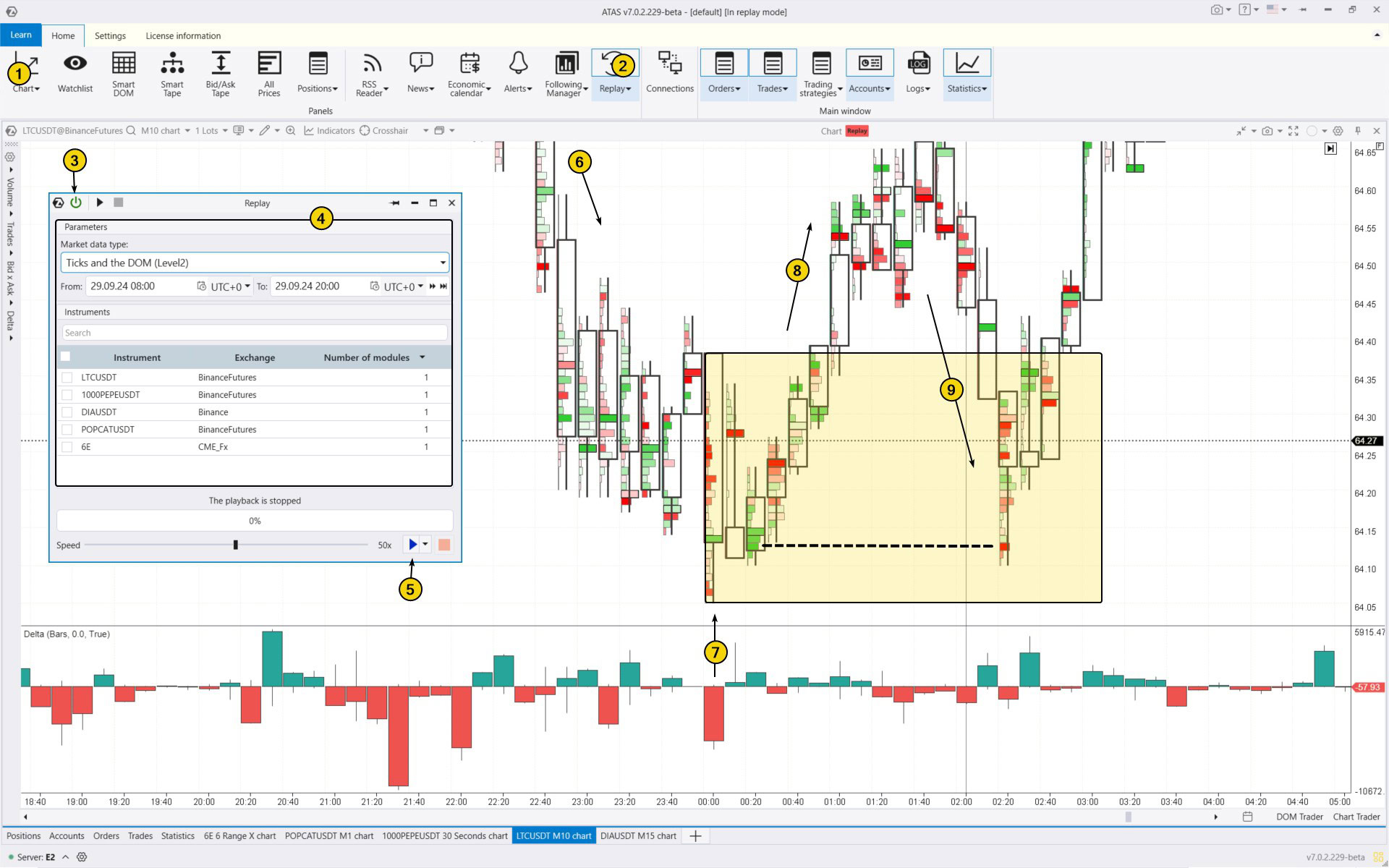
To try the simulator, download the ATAS platform for free, install, and launch it, and then:
- Open a chart of a financial instrument.
- Click on the Market Replay button in the main ATAS menu.
- Activate the Replay mode (the icon should turn green).
- Adjust settings if needed (date and data type).
- Start the playback and monitor when an Order Block appears on the chart to open a position during its test.
In the Litecoin chart example below, the price starts in a downward trend (6), but by 23:00, the bearish momentum begins to slow down. A spike in selling activity is marked by number (7) on the candle, from which the yellow Order Block area is drawn. The subsequent price increase (8) validates this area and sets the stage for a test that occurs and proves successful, as the price surges after a decline (9), remaining above the Order Block area.
There is an interesting detail. At the lowest point of the test on the 02:20 candle, there is a bright red cluster at the same level where there were previously bright green buying clusters (some long positions were probably closed at break-even).
When practicing trading patterns in the Market Replay simulator, you can:
- adjust the playback speed, and pause;
- analyze footprint charts;
- use over 400 indicators, for example, the Market Profile can help you identify an Order Block pattern;
- use Chart Trader and other features to trade on the Replay built-in demo account, and then analyze your performance;
- use drawing objects, for example, mark support and resistance levels;
- use exit strategies;
- do a lot of other things to learn how to effectively use the imbalances between buys and sells.
ATAS enables you to load tick-by-tick data from cryptocurrency, stock, and futures markets, providing a comprehensive basis for analyzing price and volume interactions. This helps identify patterns when studying ICT Smart Money Concept trading strategies.
Conclusions
The Order Block pattern was described and popularized by American trader and analyst Michael Huddleston, who is better known as The Inner Circle Trader (ICT). He runs a popular YouTube channel where he promotes his Smart Money Concept, which includes the Order Block pattern.
What Are the Advantages of an Order Book?
✔ Using Order Blocks helps traders gain a better understanding of market structure and price dynamics, as the strategy focuses on analyzing the intentions of major players (Smart Money).
✔ Order Blocks offer the opportunity to enter a trade before the trend starts.
✔ They naturally complement volume analysis, providing strong confirmations of Smart Money activity.
What Are the Risks Associated with the Order Block Strategy?
✘ The pattern can sometimes be false. A breakout of an Order Block may lead to the formation of a Breaker Block, which can also be a false signal.
✘ Successfully trading Order Blocks requires experience and skill in assessing market context to understand the intentions of Smart Money players, which can be challenging for beginners.
✘ Since candlestick formations are used to identify and trade Order Blocks, nuances related to timeframes and the positioning of OHLC prices can complicate the analysis.
Download ATAS. It is free. Once you install the platform, you will automatically get the free START plan, which includes cryptocurrency trading and basic features. You can use this plan for as long as you like before deciding to upgrade to a more advanced plan for additional ATAS tools. You can also activate the Free Trial at any time, giving you 14 days of full access to all the platform’s features. This trial allows you to explore the benefits of higher-tier plans and make a well-informed purchasing decision.
Do not miss the next article on our blog. Subscribe to our YouTube channel, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Telegram or X, where we publish the latest ATAS news. Share life hacks and seek advice from other traders in the Telegram group @ATAS_Discussions.
Information in this article cannot be perceived as a call for investing or buying/selling of any asset on the exchange. All situations, discussed in the article, are provided with the purpose of getting acquainted with the functionality and advantages of the ATAS platform.