Tokenomics (combining “token” and “economics”) explains how economic models operate within blockchain projects. This concept focuses on the issuance and circulation of digital tokens, along with the supply and demand factors that impact their value and usage.
Studying the tokenomics of various cryptocurrency projects helps to understand how they interact with the market and how promising the project’s assets may be for an investor.
Read more:
Tokenomics: What Is It?
A token is a digital asset created and maintained by a project on a blockchain. While the term “token” is often used as a synonym for “cryptocurrency,” there is a subtle difference: each cryptocurrency has its own blockchain, whereas tokens can be issued on another blockchain, like Ethereum.
Tokenomics, simply put, covers everything related to how a digital asset functions, including its creation, distribution, circulation, and its role in achieving the project’s goals.
Tokenomics describes the ecosystem and conditions in which tokens operate. It also applies to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, encompassing all aspects of their operation.
Tokenomics in Practice: A Real-Life Analogy
Imagine you start a fitness club (a blockchain project) and issue membership cards (tokens).
When designing the “tokenomics of your club,” you would need to consider questions like:
- How many membership cards will be issued?
- Will the number of cards change over time?
- Will the cards be different or identical?
- Who will receive them, and how?
- What value does the card represent?
- Can the card be given to others, and if so, how?
In reality, tokenomics in cryptocurrency can be quite complex, involving factors similar to real-world concepts like inflation and deflation, money multiplier, central bank interventions, budget balancing, currency reserves, and more.
Why Is Tokenomics Important?
For investors and users, understanding tokenomics is crucial for making informed decisions about buying, selling, or using tokens.
For project creators, tokenomics serves as a tool to encourage desired user behavior, generate interest in the project, and achieve various goals.
Key Tokenomics Terms and Their Meanings
Inflation Rate — the rate at which new tokens are created, indicating the pace of inflation.
Deflationary Mechanism — a system designed to reduce the total number of tokens in circulation, often through token burning.
Token Burning — the process of permanently removing tokens from circulation to decrease the total supply, which can potentially increase their value.
For example, 0.7 ETH is burned every minute:

Smart Contract — a programmable contract often used to manage tokens. It automatically executes the conditions and functions built into it.
Airdrop — the free distribution of tokens to community members or users, typically to generate interest in a project or reward loyal users.
Example. In 2018, Stellar, a platform for cross-border payments, conducted one of the largest airdrops in history, distributing around 2 billion XLM tokens. Anyone who registered on Blockchain.com and verified their identity received tokens. The goal was to increase the spread of Stellar tokens and encourage their use in various applications and services.
ICO (Initial Coin Offering) — an initial coin offering, a way to raise funds for a new cryptocurrency project by selling tokens.
IEO (Initial Exchange Offering) — an initial coin offering conducted through a cryptocurrency exchange, where the exchange manages the sale of tokens.
Minting Tokens — the process of creating new tokens and bringing them into circulation.
Circulating Supply — the number of tokens currently in circulation and available for trading.
Total Supply — the total number of tokens planned for issuance (including those already created and those to be created in the future).
Market Cap — the total market value of all tokens in circulation, calculated by multiplying the current token price by the total number of tokens in circulation.
Liquidity — the ability of tokens to be quickly converted into USDT, BTC, or other valuable assets without a significant loss in value.
Vesting Schedule — a plan that outlines when and in what amounts tokens become available to their holders. In cryptocurrency, vesting acts as a safeguard against a sudden drop in value if holders decide to sell a large number of tokens at once.
Token Distribution — the process of distributing tokens among project participants, including teams, investors, and users.
Example. Here is how assets were distributed at the launch of projects like ETH, SOL, DOT, and others, according to Messari. The distribution included allocations for investors, the project team, and efforts to attract users through airdrops and rewards.
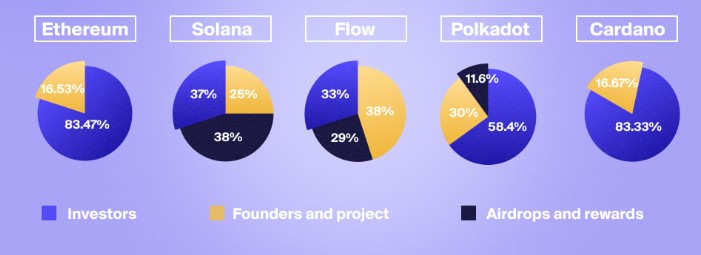
Careful token distribution provided a strong boost at the start of a project.
A token is a digital asset that represents value or rights within a blockchain project. It can be used to access project services, participate in governance, or act as a medium of exchange.
Popular Types of Tokens:
Utility Token. A token that grants access to products or services within a specific project or platform.
Examples:
- Basic Attention Token (BAT) is used in the Brave browser to reward users for viewing ads and to facilitate payments from advertisers.
- Filecoin (FIL) is used to pay for data storage and retrieval in the decentralized Filecoin network.
Security Token: A token that functions as an investment instrument and may be regulated like a security.
Governance Token: A token that gives holders the right to participate in the project’s decision-making process, vote on changes, and make proposals.
Example. UNI – the governance token for the decentralized exchange Uniswap, which allows holders to vote on changes to the protocol.
Advantages of Well-Designed Tokenomics in Cryptocurrencies
Effective tokenomics can attract investors by offering transparency, stability, and growth potential for tokens. It also positively impacts:
✔ Maintaining token value. Good tokenomics helps keep token value stable through mechanisms like inflation and deflation controls, as well as opportunities for passive income (staking), and more.
✔ Community engagement. Tokenomics encourages early participation and keeps users, developers, and other members of the ecosystem active and involved over time.
✔ Ecosystem stability. Proper token distribution and management support project development. Tokenomics can also add extra value to tokens, further strengthening the project.
Potential Issues with Poor Tokenomics
A poorly designed tokenomics model can deter investors, potentially leading to funding shortages and a slowdown in the project’s development. Other issues include:
✔ Volatility and instability. Ineffective token distribution can create vulnerabilities to manipulation, liquidity problems, and sharp swings in token value. This can undermine trust in the project and increase risks for participants.
✔ Inflation and devaluation. Without effective inflation control mechanisms, tokens can quickly lose their value.
✔ Lack of incentives: If participants do not receive adequate incentives to engage with and develop the ecosystem, it can lead to decreased activity and interest in the project.
An example is shown in the screenshot below. The Cenit Finance tokenomics simulator illustrates the risks associated with poor tokenomics.
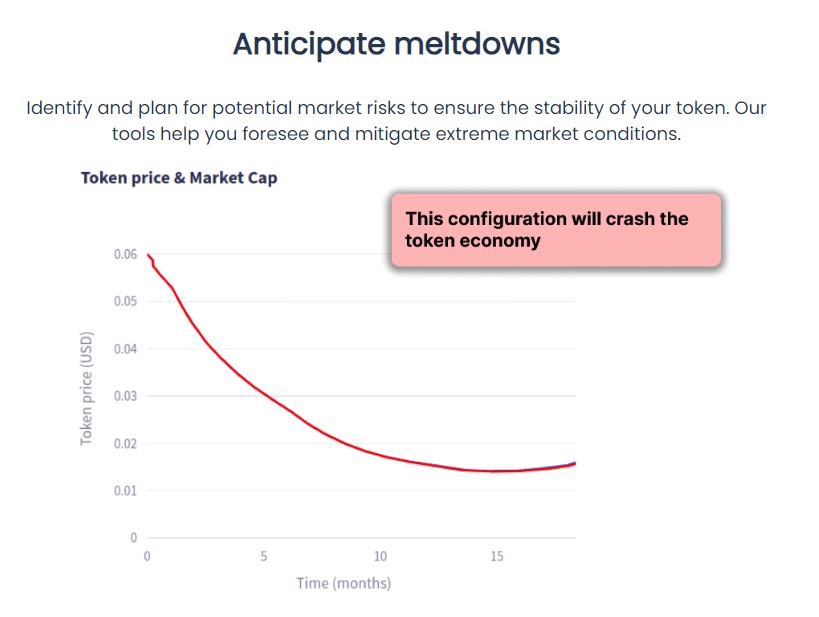
If tokenomics does not ensure token stability, it can ultimately result in the project’s bankruptcy.
Comparing Tokenomics Across Leading Projects
The table below illustrates how different the tokenomics of top-10 cryptocurrencies can be:
| Tokenomics Element | Bitcoin (BTC) | Ethereum (ETH) | Dogecoin (DOGE) | The Open Network (TON) |
| Maximum Supply | 21 million | Unlimited | Unlimited | 5 billion |
| Emission | Mining, halving every 4 years | Mining and validators (PoW and PoS) | Mining, fixed reward | Auctions, sales to investors |
| Distribution | Miners, investors, users | Investors (83.47%), creators (16.53%) | Miners, investors, users | Investors (98.55%), creators (1.45%) |
| Usage | Digital currency | Smart contracts, dApps, transactions | Payments, tips | dApps on Telegram, transactions |
Conclusions
Tokenomics is a crucial aspect of any cryptocurrency project. Information about tokenomics should be accessible and clear to all users of the project, which is why it is typically published even before the project’s official launch.
Example. Bitcoin is widely known as “digital gold” due to its limited supply (21 million coins). This aspect of tokenomics, designed by Bitcoin’s creator Satoshi Nakamoto, makes BTC a popular choice for long-term investment, enhancing its appeal to investors.
However, for short-term traders involved in crypto day trading, tokenomics is less likely to influence their trading decisions significantly.
Download ATAS for free. This program enables you to trade tokens from successful projects with strong tokenomics that have been listed on reliable crypto exchanges.
During the trial period, you will be able to experiment with various strategies using access to platform tools such as:
- DOM Levels, market profiles, and other indicators;
- ATAS Smart DOM, ATAS Smart Tape;
- a Market Replay trader simulator;
- custom time frames, flexible settings, and much more.
Once you install the platform, you will automatically get the free START plan, which includes cryptocurrency trading and basic features. You can use this plan for as long as you like before deciding to upgrade to a more advanced plan for additional ATAS tools. You can also activate the Free Trial at any time, giving you 14 days of full access to all the platform’s features. This trial allows you to explore the benefits of higher-tier plans and make a well-informed purchasing decision.
Do not miss the next article on our blog. Subscribe to our YouTube channel, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Telegram or X, where we publish the latest ATAS news. Share life hacks and seek advice from other traders in the Telegram group @ATAS_Discussions.
Information in this article cannot be perceived as a call for investing or buying/selling of any asset on the exchange. All situations, discussed in the article, are provided with the purpose of getting acquainted with the functionality and advantages of the ATAS platform.